Lung Cancer Explained. Your Guide to Understanding and Prevention
When it comes to lung cancer, the numbers tell a story that's hard to ignore.
Lung cancer is notorious not only because it's common but also because it develops quietly, without obvious symptoms, until it's quite advanced.
Consider this startling statistic: lung cancer claims more lives each year than breast, colon and prostate cancers altogether.
It is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, accounting for the highest mortality rates among both men and women. Approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases are attributed to smoking.
Such figures highlight the critical need for awareness and education.
We aim to empower you with knowledge, guiding you through the complex landscape of lung cancer, from its onset to its management and, most crucially, its prevention.
Don't face lung cancer alone. My 1Health connects you to a global network of advanced hospitals and specialised oncologists. Get expert care now!
Consult some of the leading oncologists in India for a virtual consultation. Start your treatment today.
What is Lung Cancer?
Understanding Lung Cancer and Its Types
Lung cancer occurs when cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably, leading to serious health complications.
It starts in the lungs and can spread to other parts, such as lymph nodes and the brain.
Interestingly, cancers from other organs can also spread to the lungs. These are known as metastases.
There are two types of lung cancer: small cell and non-small cell lung cancer.
Non-small cell lung cancer includes adenocarcinoma, which commonly affects people who have never smoked, and squamous cell carcinoma, which often starts in the bronchi.
Non-small cell lung cancer is more common and grows slowly compared to small cell lung cancer.
Small cell lung cancer, almost always linked to cigarette smoking, is a fast-growing type that spreads quickly.
b. How Does Lung Cancer Develop?
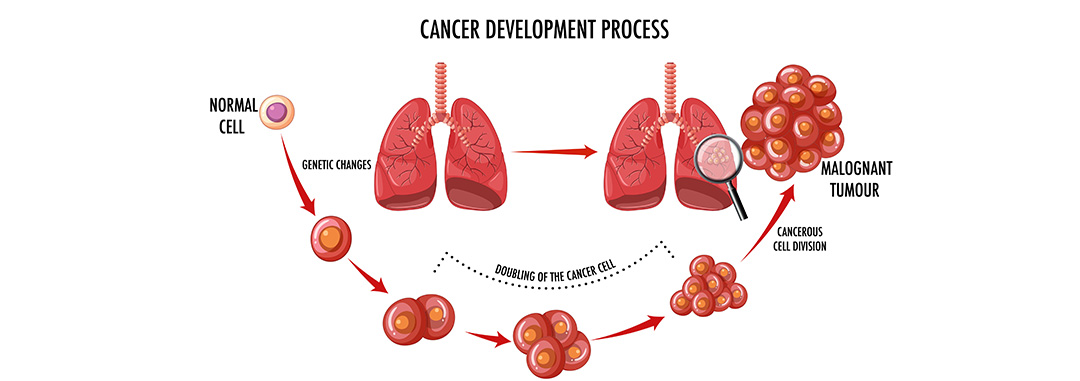
To understand how lung cancer develops, it's helpful to know about the lungs' function and structure.
Our lungs, divided into lobes, bring oxygen into the body and expel carbon dioxide.
They comprise different types of cells, including epithelial cells, which line the airways and produce mucus and other cells involved in lung structure and function.
Cancer develops due to mutations in normal lung cells. These mutations disrupt the cells' natural growth and death cycle, leading to uncontrolled division and an overabundance of cells.
The result is a mass or tumour, which can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
If the tumour cells invade normal tissues and originate from the lung, it is considered lung cancer.
Lung cancer can spread to other body parts, including bones and the brain.
However, if cancer spreads from another body part to the lung, it's not classified as lung cancer.
Read: Top 5 Hospitals for Lung Cancer Treatment in India
Causes and Risk Factors of Lung Cancer
Recognising what increases the risk of lung cancer is crucial for prevention and early awareness. Let's explore the primary factors:
a) Smoking
Smoking is the number one cause of lung cancer. The longer you smoke and the more cigarettes you consume, the greater your risk.
However, it's never too late to quit - stopping smoking can significantly reduce your chances of developing lung cancer.

b) Second-hand Smoke
Even for non-smokers, being around others who do can increase your risk. Non-smokers exposed to second-hand smoke are still vulnerable to lung cancer.
c) Radon Gas Exposure
This invisible gas, formed naturally in soil, rock, and water, is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. Radon can enter buildings and accumulate, posing a severe health risk over time.
d) Workplace Hazards
Certain substances you might encounter at work, like asbestos, arsenic, and chromium, can increase lung cancer risk. This risk is amplified if you smoke.
e) Family History and Genetics
If lung cancer runs in the family, your risk may be higher. Could be due to shared genetic factors or similar environmental exposures.
f) Previous Radiation Therapy
Those who have undergone radiation treatment to the chest for other cancers may find themselves at an elevated risk for lung cancer.
g) Diet and Supplements
The role of diet in lung cancer risk is complex. Notably, smokers taking beta-carotene supplements may face a higher risk.
Additionally, arsenic levels in drinking water, particularly from private wells, can also be a contributing factor.
Understanding these factors can empower you to take proactive steps in lung cancer prevention and stay vigilant about early detection.
Recognising the Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Identifying Early Warning Signs
Lung cancer often doesn't show symptoms in its early stages, making early detection challenging.
However, recognising the following symptoms, especially if they persist, is crucial as they could indicate the presence of lung cancer:
a) Persistent Cough
b) Blood in Sputum
c) Breathing Difficulties
d) Chest Discomfort
e) Voice Changes
f) Unintended Weight Loss
g) Persistent Fatigue
h) Recurrent Infections
i) Wheezing
Suppose lung cancer spreads to other parts of the body. In that case, additional symptoms may include:
a) Bone pain
b) Neurological changes (like headaches or dizziness)
c) Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
d) Swollen lymph nodes
If you notice any lung cancer symptoms, seeing a doctor immediately is vital. Early detection can make a significant difference in the effectiveness of treatment.
Uncertain about symptoms? Talk to a My 1Health specialist: Get personalised guidance from our dedicated support team.
Diagnosing Lung Cancer Stages
Understanding the Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing lung cancer accurately is crucial to determining the best treatment plan. Here are the steps involved in diagnosing lung cancer:
1. Imaging Tests. The initial step usually involves imaging tools such as:
- CT Scans. These use X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the chest.
- MRI Scans. Utilising radio waves and magnets, MRI scans produce detailed images of the chest's soft tissue, helping to see if the cancer has spread.
- PET Scans. These involve injecting a substance to highlight cancer cells and are helpful for checking if cancer has spread.
2. Biopsies and Other Tests. If imaging suggests the possibility of cancer, doctors may perform additional tests.
- Biopsies. The most common method for diagnosing lung cancer is where tissue samples are taken for examination.
This can be done through needle biopsies, guided by CT scans, or via bronchoscopy.
- Bronchoscopy. A tube passed down the throat to examine the lungs and take tissue samples. This can be done with sedation or general anaesthesia.
- Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS). A type of bronchoscopy that uses ultrasound to examine the chest cavity and take tissue samples.
- Mediastinoscopy. A surgical procedure to examine the area between the lungs and take biopsies, typically under general anaesthesia.
Fast-track your diagnosis with My 1Health: Connect with a lung specialist for advanced diagnostics efficiently.
Staging the Cancer
Once lung cancer is diagnosed, it is staged. Staging involves determining the size of the tumour and whether it has spread beyond the initial site.
This information is vital for choosing the most effective treatment plan.
a) Stage 0
Also known as carcinoma in situ. The cancer cells are only in the top layers of cells lining the air passages and haven't invaded deeper into lung tissue or spread outside the lung.
b) Stage I. Cancer is localised within the lung and hasn't spread to lymph nodes.
c) Stage II. Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or into the chest wall.
d) Stage III. Cancer has spread more extensively within the lung, to nearby areas, or more lymph nodes.
e) Stage IV. The most advanced stage is where cancer has spread to distant parts of the body.
Treatment Options for Lung Cancer
1. Surgery. This involves removing cancerous tissue from the lung. Types of surgeries include:
a) Wedge Resection- Removing a small section of the lung containing the tumour.
b) Segmental Resection- Removing a larger lung portion.
c) Lobectomy- Removing an entire lung lobe.
d) Pneumonectomy- Removing an entire lung.
2. Chemotherapy
Drugs are used to shrink or kill cancer cells, either through oral medications or intravenous injections.
It can be used before surgery to shrink the tumour, after surgery to remove any remaining cancer cells, or as the primary treatment in advanced cases.
3. Radiation Therapy
High-energy rays are used to kill cancer cells.
It can be used before or after surgery, often combined with chemotherapy or as a standalone treatment for advanced lung cancer to relieve symptoms.
4. Targeted Therapy
These drugs target specific aspects of cancer cells to block their growth and spread. They are generally used for cancers with certain genetic mutations.
5. Immunotherapy
This approach uses the body's immune system to fight cancer. It's typically reserved for advanced lung cancers.
6. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (Radiosurgery)
An intense radiation treatment targeting the cancer from multiple angles. It's an option for small lung cancers or for treating lung cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
7. Palliative Care
Focuses on providing relief from the symptoms and stress of lung cancer. It can be used alongside other treatments to improve quality of life.
Get a FREE personalised treatment plan, supported by expert guidance. Explore options, connect with oncologists, and find the best path forward.
Factors Influencing Treatment Decisions
Treatment choices are influenced by several factors.
a) The cancer's type and stage.
b) The patient's overall health.
c) Personal preferences regarding treatment goals and quality of life.
Some patients might opt for comfort care, focusing solely on symptom relief, particularly in advanced stages where treatment side effects may outweigh benefits.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Patients can also explore lifestyle adjustments and home remedies to manage symptoms like shortness of breath.
These include relaxation techniques, finding comfortable positions, focusing on breathing, and conserving energy for essential activities.
Life with Lung Cancer
Living with lung cancer presents unique challenges and affects daily life in various ways, depending on the stage and treatment. To cope and find support, consider:
a) Communicating with Loved Ones
Engage in open conversations with friends and family and connect with other family and a similar situation.
b) Lung Cancer Specialist Nurses
Seek support from specialist nurses who can provide information and guidance on managing lung cancer.
c) Managing Breathlessness
Simple measures like breathing exercises, adjusting daily activities, and using a fan can help manage breathlessness.
Medication and oxygen therapy may be options for severe cases.
d) Pain Management
Pain varies among individuals and can be managed through palliative care, which may include medication and supportive therapies.
e) Emotional Well-being
Acknowledge and address emotions that come with cancer, from shock and anxiety to sadness and depression. Openness and honesty about your feelings are crucial.
f) Finding Support
Talk to counsellors psychologists, or join support groups to share experiences and get emotional support.
g) Comprehensive Care
In advanced stages, palliative care provides support and pain relief. This includes managing symptoms and ensuring comfort at home, in a hospital, or in a hospice.
Ready to face lung cancer with confidence? Take control of your journey with My 1Health.
Connect with your personalised Patient Support Specialist and access emotional support and expert guidance. It's time to breathe easier.
Preventing Lung Cancer
a) Smoking Cessation. Quitting smoking is the most effective way to lower lung cancer risk. If you've never smoked, don't start, and talk to children about the dangers of smoking.
b) Avoid Second-hand Smoke. Stay away from environments where others smoke. Encourage smokers in your vicinity to smoke outside or quit.
c) Radon Testing. Test your home for radon, especially if you live where radon is known to be a problem.
d) Workplace Safety. Protect yourself from workplace carcinogens. Follow safety measures and use protective gear as required.
e) Healthy Diet and Exercise. Adopt a diet rich in fruits and vegetables and exercise regularly.
f) Regular Cancer Screenings. Regular screenings can help detect lung cancer early, especially for those at high risk.
My 1Health: Specialised Lung Cancer Care on a Global Scale
Access to Global Lung Cancer Experts
My 1Health is dedicated to transforming the experience of those facing lung cancer, extending our reach well beyond Africa to a global network.
We specialise in connecting patients with leading lung cancer specialists and JCI-accredited hospitals worldwide.
We aim to provide you with unparalleled access to advanced treatments and expert care, ensuring the best possible outcomes for those battling lung cancer.
My 1Health App: Personalised Lung Cancer Care at Your Fingertips

Navigating lung cancer treatment is made simpler with the My 1Health app.
This all-encompassing platform is a gateway to world-class lung cancer care, offering streamlined access to elite doctors, managing treatment schedules, and maintaining health records.
Every lung cancer patient is paired with a dedicated support specialist, offering personalised care and guidance throughout your treatment journey.
By downloading the My 1Health app, you gain a supportive partner, ensuring you and your loved ones receive comprehensive care and support no matter where you are.
Download the My 1Health App on App Store or Google Play and simplify your healthcare journey.
In summarizing our comprehensive exploration of lung cancer, the key takeaway is the pivotal role of early detection and proactive treatment in enhancing survival rates.
We've covered the causes, symptoms, stages, and treatments of lung cancer, underscoring the value of support systems and lifestyle changes in managing and preventing this disease.
Individuals must be aware of lung cancer risks, adopt preventive measures like smoking cessation and regular screenings, and promptly seek medical advice for any concerning symptoms.
These efforts can significantly impact the fight against lung cancer, leading to earlier detection, more effective treatment, and ultimately, better health outcomes.
Read a related article: Top 5 Hospitals for Lung Cancer Treatment in India