Breast cancer is a medical condition that affects millions of lives globally. It is a malignant growth that occurs in the breast tissue, often spreading alarmingly.
While predominantly affecting women, accounting for approximately 25% of all cancer cases in this demographic, men are not entirely immune. Although the disease is rare in men, it does occur.

According to Breast Cancer Now, men should also be body-aware and look for similar signs as women, such as lumps or changes in breast tissue. Awareness and regular check-ups are crucial for early detection in both genders.
This comprehensive guide aims to enlighten you on the early signs, risk factors, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options for breast cancer.
What are the Early Signs of Breast Cancer?
Early detection can be a game-changer in the fight against breast cancer. However, many individuals remain unaware of the early symptoms, leading to late-stage diagnosis.

The World Health Organization emphasises the importance of early detection and has designated October as Pink Month for breast cancer awareness. Here are the signs you should never ignore:
1. Breast Lumps
The most common and noticeable sign is the formation of a lump in the breast. These breast cancer lumps are often painless and complex, although some may cause a prickly sensation. Lumps are usually visible on a mammogram long before they can be seen or felt.
2. Changes in Breast Appearance
Any unexplained change in the breast's size, shape, or appearance should be a cause for concern. This could manifest as swelling, shrinkage, or asymmetry between the breasts.
3. Nipple Changes
An inverted nipple or any unusual discharge from the nipple can be a sign of breast cancer. While nipple discharge can also be due to other factors, any persistent discharge should be checked immediately.
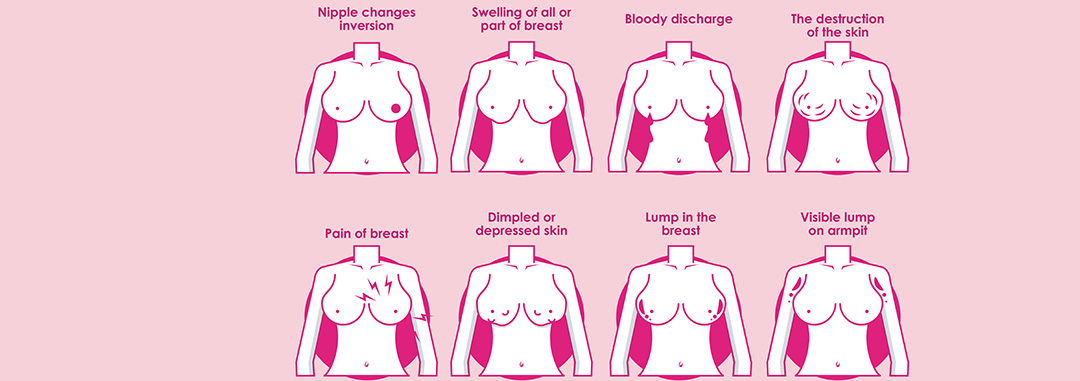
4. Skin Irritation or Dimpling
Skin irritation or dimpling on the breast can indicate inflammatory breast cancer, a rare but aggressive form. Dimpling refers to a puckering of the skin that resembles the skin of an orange. If you notice any persistent redness or pitting of the skin over your breast, consult a healthcare provider.
5. Pain in the Breast or Nipple
While pain in the breast or nipple is commonly associated with menstrual cycles, persistent pain that does not go away should be evaluated.
Book a Consultation for a Second Opinion
How Does One Get Breast Cancer?
Understanding breast cancer's root causes or risk factors can be a pivotal step in prevention and early detection. While some factors are beyond our control, such as age and genetics, others can be managed.
Here are the causes of breast cancer:
a) Hormonal Imbalance- Elevated estrogen levels can contribute to the rapid multiplication of cells, increasing the risk of breast cancer. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT), commonly used to manage menopausal symptoms, has also been linked to increased risk.
b) Radiation Exposure- Exposure to high radiation levels, especially at a young age, can elevate the risk.
c) Unhealthy Diet- A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can increase the risk of breast cancer. On the other hand, a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help in prevention.
d) Age Factor- As you age, the risk of developing breast cancer increases, making age a significant factor.
e) Prior Breast Conditions- A history of breast conditions like lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) or atypical hyperplasia elevates your risk.
f) Personal History of Breast Cancer- If you've previously been diagnosed with breast cancer, the likelihood of recurrence in the opposite breast is higher.
g) Family Medical History- While most breast cancer patients have no family history, having a close relative diagnosed, especially at a young age, can increase your risk.
h) Obesity- Excess weight, particularly post-menopause, is a known risk factor for breast cancer.
i) Early Menstruation- Starting your menstrual cycle before age 12 can increase the risk.
j) Late Menopause- Women who enter menopause at an older age are more susceptible.
k) Late or No Pregnancy- Giving birth to your first child after 30 or never pregnant can elevate the risk.
l) Alcohol Consumption- Regular drinking has been linked to a higher risk of breast cancer.
Read More: Cancer Treatment in Thailand
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is the first step towards effective treatment. Here are some diagnostic methods:
1. Clinical Breast Examination
This is often the first test done when a lump is found. The doctor will physically examine the breast and armpit for any lumps or abnormalities.
2. Mammography
This is an X-ray of the breast and effectively detects breast cancer early.
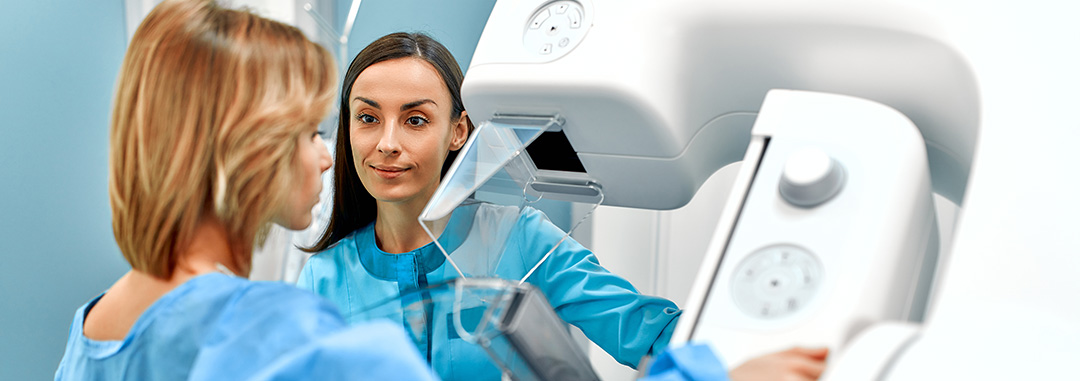
3. Breast Ultrasound
This determines whether a lump is a solid mass or a fluid-filled cyst. Ultrasounds are often used with mammograms to get a more accurate diagnosis.
4. Biopsy
In a biopsy, a small tissue sample is taken from the suspected area to be examined under a microscope. This is the most definitive way to diagnose breast cancer.
5. MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging is used for high-risk women and provides a more detailed image than a mammogram.
6. Blood Tests
Certain markers like CA 15-3, CA 27-29, and CEA can be elevated in people with breast cancer, although they can also be upgraded for other reasons.
Consult our top specialists and explore treatment options today!
Best Treatment Options for Breast Cancer
Treatment options have evolved over the years, offering hope to many. Here are some of the most effective treatment options available today:
1) Surgical Procedures
Surgery is often the first line of treatment and can range from a lumpectomy, where only the lump is removed, to a total mastectomy, where the entire breast is removed.
2) Radiotherapy
This involves the use of high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells. It's often used after surgery to kill any remaining cells.
3) Chemotherapy
This involves using drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from dividing. Chemotherapy is often used in conjunction with other treatments.
4) Hormone Therapy
This is used for cancers that are sensitive to hormones. Drugs like Tamoxifen block the cancer cells from receiving the hormones they need to grow.
5) Targeted Therapy
These drugs identify and attack specific cancer cells without harming normal cells. They are usually used for late-stage or recurrent cancers.
6) Immunotherapy
This relatively new form of treatment boosts the body's natural defences to fight cancer. It's used for advanced and recurrent breast cancer.
What Can I Do to Reduce My Risk of Breast Cancer?
Prevention is the best form of defence. Here are some strategies:
a) Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are known carcinogens and can increase your risk of developing breast cancer.
b) Balanced Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help lower the risk of breast cancer. A high-fibre, low-fat diet is often recommended.
c) Regular Exercise
Physical activity can help you maintain a healthy weight, lowering your risk of breast cancer. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.

d) Regular Screenings
Early detection is critical to effective treatment. Regular screenings, including mammograms for women over 40, can help detect breast cancer in its early stages.
Conclusion
Understanding breast cancer is the first step towards effective prevention and treatment. As we have explored the early signs, risk factors, and prevention methods, it becomes clear that awareness is our greatest ally.
While the path may be daunting, it's crucial to remember that timely intervention and informed choices can significantly alter the course of this disease. Let's stay vigilant and proactive, for in the realm of breast cancer, knowledge truly is power.
Book a mammogram screening test today!